October is a timely moment to put our health first. Breast cancer caught early is more treatable, and national guidance has recently shifted to make screening more consistent and accessible.
Who should get screened—and when?
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends that people at average risk begin screening mammography at age 40, every other year through age 74. This 2024 update responds to rising diagnoses in people in their 40s and aims to reduce mortality, especially among Black women, who face higher death rates. If you’re 40–74 and at average risk, talk with your clinician about getting (or staying) on a biennial schedule. Those with higher-than-average risk (e.g., certain gene variants, strong family history, prior high-dose chest radiation) should discuss earlier or additional screening with their providers.
How does this compare with other guidance?
The American Cancer Society (ACS) recommends that people ages 40–44 may choose annual mammography; ages 45–54 should get annual mammograms; and ages 55+ may continue annual screening or switch to every two years as long as they are in good health and have a life expectancy of at least 10 years. If you previously followed ACS’s annual schedule, it’s reasonable to continue—what matters most is that you and your clinician align on a plan that fits your risk and preferences.
Why mammograms—and what should I expect?
For most people of screening age, mammograms are the best tool to find cancer early, before it’s large enough to feel or cause symptoms; regular screening lowers the risk of dying from breast cancer. Expect brief compression that can be uncomfortable, but it typically lasts only moments. Scheduling shortly after your period may reduce tenderness.
Know the warning signs between screenings.
Contact your primary care provider or clinician if you notice a new lump, swelling, skin dimpling or irritation, nipple changes (inversion, discharge, or pain), redness/flaking, a change in breast size/shape, or pain that doesn’t go away. Screening is vital, but knowing your baseline—and speaking up when something is different—matters too.
Benefits resources
Kalamazoo College provides a rich, comprehensive benefits package to help you stay healthy and well—but it only helps if you use it. Leveraging your benefits can save you money, and in some cases, save your life.
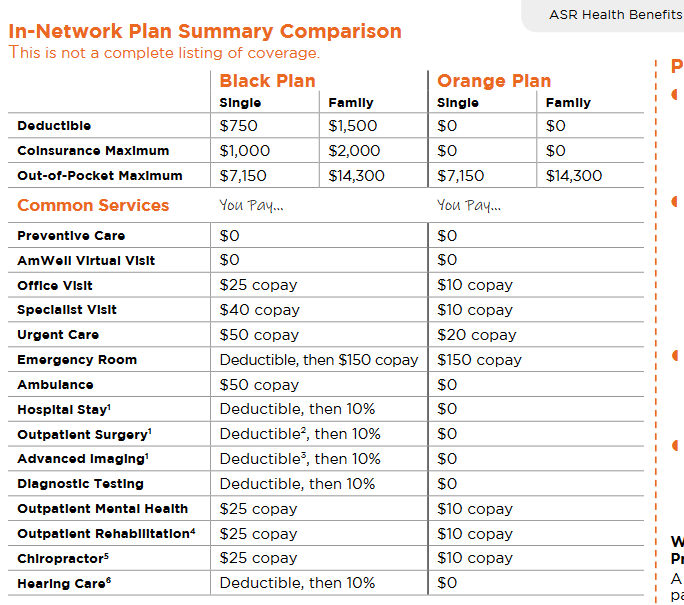
- Preventive screenings at no cost: Screening mammograms are covered at 100% on both the Black and Orange medical plans (when billed as preventive care and using in-network providers).
- $50 screening reward: Earn a $50 reward for mammograms when you enroll in ASR’s Healthcare Choices + Rewards program and schedule with a provider marked by the green trophy. (Program terms apply. Please click on the link for more information)
- Support for you and your family: If you’re caring for someone with a diagnosis—or navigating your own treatment—contact our Employee Assistance Program (EAP) for confidential counseling, caregiver resources, and referrals.
Support for survivors and those in treatment.
Life after a breast cancer diagnosis involves medical follow-up and whole-person support. Survivorship care plans help you track appointments, late effects, and healthy lifestyle goals; reputable tools and guidance are available through the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and American Cancer Society. Peer communities like Living Beyond Breast Cancer (LBBC) offer helplines and online groups to connect you with trained volunteers and others who understand the journey. Consider sharing these resources with a colleague or loved one.
What to do this month
- If you’re 40+ and due (or never started), book a screening mammogram.
- If you’re at higher risk, ask your clinician about an individualized plan.
- If you’re a survivor, request a written survivorship care plan and share it with all your providers.
- Share vetted resources with friends and family; your encouragement can make the difference in someone scheduling their screening.
Early detection saves lives. Whether you are scheduling your first mammogram, staying on track with regular screenings, or navigating life after treatment, you’re not alone—and support is available.
References
- American Cancer Society. (2023, November 1). American Cancer Society guidelines for the early detection of cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/screening/american-cancer-society-guidelines-for-the-early-detection-of-cancer.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024, September 16). Screening for breast cancer. https://www.cdc.gov/breast-cancer/screening/index.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2024, September 11). About mammograms. https://www.cdc.gov/breast-cancer/about/mammograms.html
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2025, July 30). Symptoms of breast cancer. https://www.cdc.gov/breast-cancer/symptoms/index.html
- Living Beyond Breast Cancer. (n.d.). Breast Cancer Helpline. https://www.lbbc.org/community/breast-cancer-helpline
- National Cancer Institute. (2024, December 2). Follow-up medical care for cancer survivors. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/coping/survivorship/follow-up-care
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. (2024, April 30). Final recommendation statement: Screening for breast cancer. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/announcements/final-recommendation-statement-screening-breast-cancer-0
- U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. (2024). Recommendation: Breast cancer: Screening. https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/breast-cancer-screening